originally posted at https://canmom.tumblr.com/post/700938...
I think you could say I tend to like three different sources of comic. One is webcomics. The second is manga (and also manhwa). The third? Comics written by a wizard in the 1980s.
You see, most of the real ‘classic’ comics from this period are by some sort of wizard. Alan Moore? Famously a magician and really looks the part. Grant Morrison? Chaos magician. Alejandro Jodorowsky? Read the last first post in this series lmao.
It’s not actually all that surprising since comics are an incredibly densely symbolic medium which give you a pretty direct line of attack on the collective unconscious, if you believe in that. Being a wizard is probably pretty good training for writing interesting comics. Or maybe Alan Moore’s success just kicked off a fad of trying to find more British wizards to move comics off the shells at DC - pretty much Morrison’s own account of their introduction into the world of comics.
And that brings us to…
Animal Man
(1988-95, written by Grant Morrison, pencilled Chas Truog, Tom Grummett and Paris Cullins, inked Doug Hazlewood, Mark McKenna, Steve Montano and Mark Farmer, coloured Tatjana Wood and Helen Vesik, lettered by John Costanza and Janice Chiang, covers illustrated by Brian Bolland… phew…)

So. Animal Man! Basically the story as Morrison tells it in the intro to the collected edition is…
In 1987, at the height of the critical acclaim for Alan Moore’s work on SWAMP THING and WATCHMEN, DC Comics dispatched a band of troubleshooters on what is quaintly termed a “headhunting mission” to the United Kingdom. The brief was to turn up the stones and see if there weren’t any more cranky Brit authors who might be able to work wonders with some of hte dusty old characters languishing in DC’s back catalogue. As one of those who received the call that year, I had no idea who I might dig up and revamp. On the Glasgow to London train, however, my feverishly overstressed brain at last lighted upon Animal Man. This minor character from the pages of STRANGE ADVENTURES in the ‘60s had always, for heaven only knows what murky reasons, fascinated me and, as the train chugged through a picturesque language of Tudor houses and smiling bobbies on bicycles, I began to put together a scenario involving an out-of-work, married-with-children third-rate superhero who becomes involved with animal rights issues and finds his true vocation in life.
You can read the full introduction here. It’s pretty funny.
In fact, Morrison is leaving out a little of the story. The ‘headhunting mission’ took place after Alan Moore decisively cut ties with DC over issues related to royalties (particularly for merchandising) and a proposed age-rating system. He stopped writing for them after finishing the last few issues of V for Vendetta, and DC went looking for someone new to fill his niche of ‘left-wing British guy, good at prose, wizard’. Along with Morrison, they found…
Jamie Delano, who was approached by DC as the writer of the Swamp Thing spin off Hellblazer; Neil Gaiman and Dave McKean, who collaborated on the Black Orchid limited series, as well as the famous and acclaimed Sandman; Peter Milligan, who launched a new Shade, the Changing Man series; and Scottish creator Grant Morrison, whose pitch of an Animal Man series was approved. Later British creators to work on American comics include Mark Millar, Warren Ellis, Garth Ennis and Paul Jenkins.
This also comes in a time when American comics are getting more and more literary aspirations: complex characterisation, more naturalistic dialogue, less emphasis on superheroes. Which can perhaps also be attributed to Alan Moore. The ‘British invasion’ might be compared with the rise of gekiga in Japan in the 60s and 70s, although here the change was happening not in alternative magazines like Garo but the most mainstream comics. Putting in a pin in that, because I need to learn more about this period.
I came to Animal Man knowing really only one thing: that it gets increasingly metafictional, culminating in an arc where the protagonist goes and meets Grant Morrison themself. This does indeed happen and it’s cool! But before that a bunch of other stuff has to happen to set up the thematic significance of this metafiction…
Morrison is a very interesting figure who I’d like to learn a lot more about. I thought of them as another example of the ‘spend years making sequential art instead of transitioning’ archetype, but it seems maybe a little more complicated than that - I think I need to do more research before I try and say anything definitive about the many noticeable ways trans girls figure in the imagination of comics from this period, and it doesn’t factor much in Animal Man compared to say Doom Patrol.
Indeed, main character Buddy is an almost parodically Normal Dad, a blonde white man living in an American suburban house with a white picket fence and… well, 2 children, not 2.5, but you know.
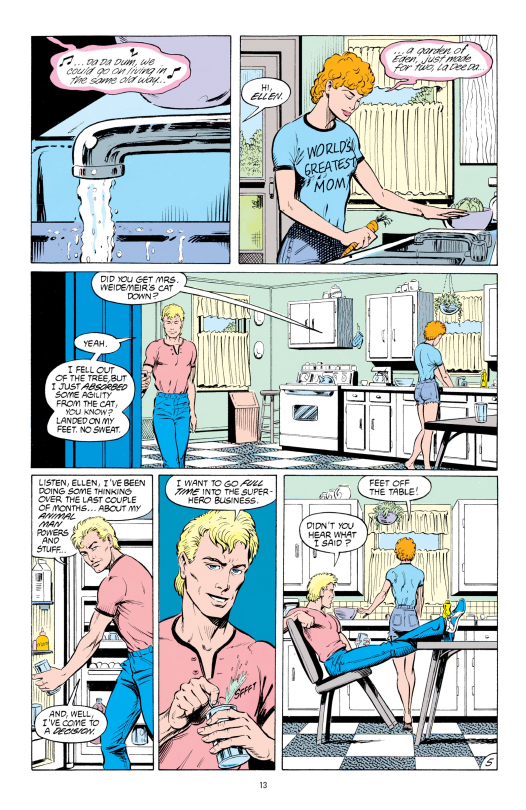
Into this world comes all sorts of weird stuff because it’s a Grant Morrison comic, and a lot of the humour in the earlier parts of the comic comes from the idea of shining a look at the fringes of the DC universe away from the central superhero battles, with a local low-tier superhero making TV appearances and becoming a minor celebrity. I think ‘everyday life in a world where superheroes are real’ has been done a lot since then, but it’s done well here. Being a superhero for Buddy starts out as just a day job; obscure superhero teams from Morrison’s encyclopedic knowledge of DC comics history are made into obscure superhero teams in-universe as well.
I don’t read American comics nearly as often as I read manga and webcomics - working on filling in the gaps there - so it’s hard for me to comment on Truog’s art in contrast to other comics. Which means what strikes me is probably more traits of ‘American Comics’ than this one specifically, but what ho…
The immediate thing I noticed is the immense anatomical precision, particularly when it comes to drawing muscles - something I’d also been struggling with at the time I read it so I was paying attention lol. Peter Chung made an interesting remark in an interview which I’ll quote here…
I think a lot of illustrators realize—and you see this a lot in American comics as well—that if you draw costumes realistically, it’s very difficult. You end up spending all your time trying to create believable drapery. So the tendency is to draw skin-tight costumes that mold around the body. This allows you to use the body more. You see this with classical sculpture, and dancers. You try to use the expressive qualities of the human body more—that’s why sculptors prefer to work with nudes, as opposed to trying to make the clothing look accurate. Otherwise you end up concentrating on the clothing and not the person.
Fairly early on, Animal Man’s outfit is updated to include a leather jacket, and there’s a solid sense of how to handle the cloth. Here’s an action scene from fairly early on with Buddy fighting against a rat monster created by the tragic villain B’wana Beast (more on him in a bit)…
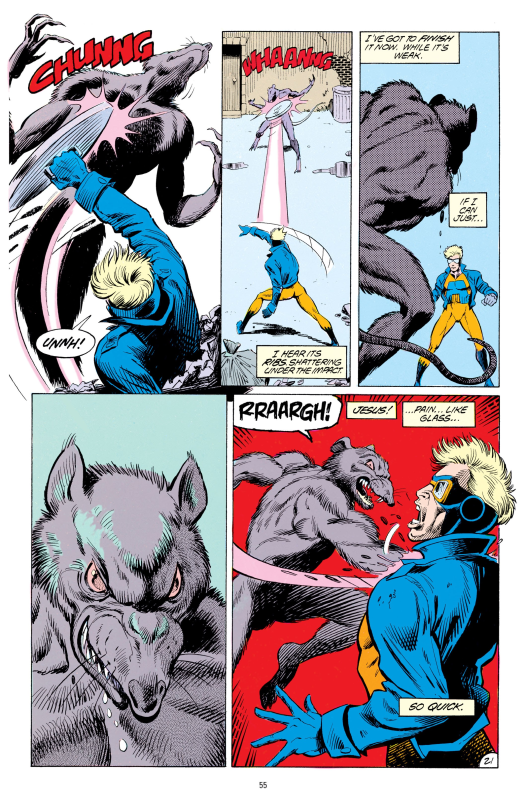

You can see how the cloth stretches at the elbow and bunches up on the inside fold. This also shows a few other aspects of the art: the shading is completely carried by hatching in the linework, with the colours being flat, either pastel or highly saturated. I think this is in part a limitation of the printing technologies of the time. There’s occasional use of screentone, as you can see on the top right panel there (which downscaling has turned into a moiré pattern…)
In comparison to manga, beyond the general differences in character design, it’s interesting to see what’s different in how action scenes are conveyed. The panelling is generally very regular and rectangular, but there will occasionally be layouts with figures overlapping the border. Some of the ways of conveying motion, like dynamic unbalanced poses, or replacing lines with perpendicular hatching, is also widely used in manga; some aren’t, such as the motion arcs you can see in the page above. There usually isn’t a lot of exaggeration or extreme perspective distortion.
I think the colouring weakens it. The colours mostly serve to separate out different volumes, but they don’t really convey much in their own right. Out of curiosity, I tried putting a page through desaturate and threshold filters to see what it would look like uncoloured. Here’s a threshold, which is what the inked page would look like…

and here’s a desaturate, which replaces the colours with pure value:
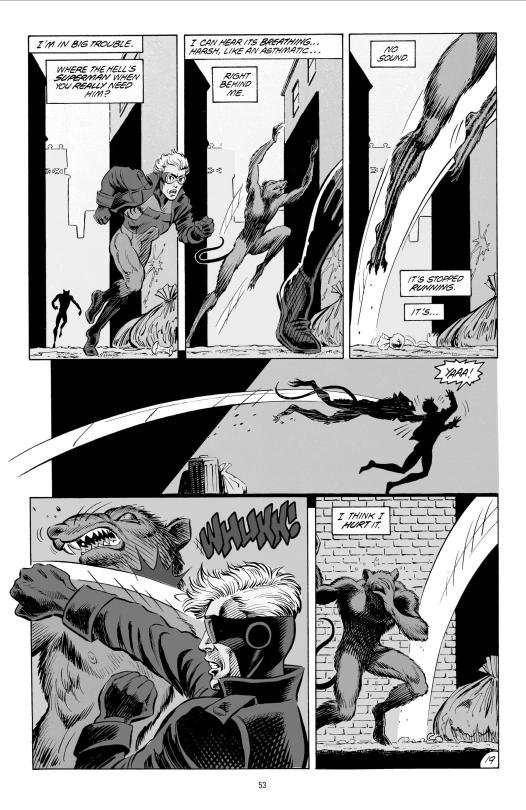

So you can see having some values to separate different elements helps, but honestly I think I prefer it desaturated lol. Still, it’s much better than the overly rendered hyper-contrast style that became popular a decade later.
The other big thing that’s different from what I’m used to in manga is the large amount of narration accompanying panels, typically but not always first-person. This is apparently something Alan Moore is responsible for establishing with V for Vendetta. I think the potential drawback with this approach is that your eyes may go straight for the text boxes, and skip the drawings entirely.
There are absolutely good sequences though, such as when Buddy and his friend the physicist
Despite these small complaints, the art generally works very well. Where it gets interesting is later in the comic when things start to get very meta, so you get a character’s deterioriation represented by using unfinished art (sketches or uninked drawings), and later messing with the formal elements like panel borders. There’s a sequence where a highly advanced Buddy fights an evil version of Superman from another timeline during a massive reality breakdown provoked by a character who is aware of all the discarded storylines and timelines in the DC universe and wants to save them, and thus you get pages like this:

Animal Man’s villains are rarely ever especially villainous, and the tone of a lot of the earlier stories is Buddy finding out about the situation and trying to prevent a tragic outcome and usually failing. Morrison used the comic to some degree to soapbox for animal rights, with early arcs dealing with animal experimentation labs and sadistic dolphin hunters. At one point he even pops by the UK to help out some hunt sabs. But it’s more using this as a source for stories than something purely didactic, and leans into conflicts like Buddy’s ambivalence when his ecoterrorist allies kill a firefighter during an attack on an animal lab as part of a broader arc of his life going to shit; he is, superhero or not, just one man who gets swept up in larger events most of the time.
Speaking of larger events, Morrison’s run on Animal Man coincided with one of DC’s periodic massive crossover events called uhh (*looks up*) Invasion!. Basically a bunch of aliens show up, so Buddy’s helping fight them; then off-screen a ‘gene bomb’ goes off which scrambles Buddy’s powers. (This also played into Morrison’s run on Doom Patrol, which I’m still reading at the moment, so more on that in the future!) The storylines associated with this event - one about an alien artist who wants to terraform the Earth, the other about a washed-up suicidal supervillain - are both good, and ‘aliens show up’ is really not far outside the usual sort of things that happen in Animal Man, but it’s funny that Grant Morrison, at the time ‘just’ an up-and-coming new writer at DC comics, is now probably the only reason that this whole event is still remembered in 2022.
Anyway, let’s get into the metafiction stuff. The story is full of DC deep cuts, and Morrison seems to be very interested in how fictional characters are constructed, how they relate to their readers, how their stories are affected by the outside world…
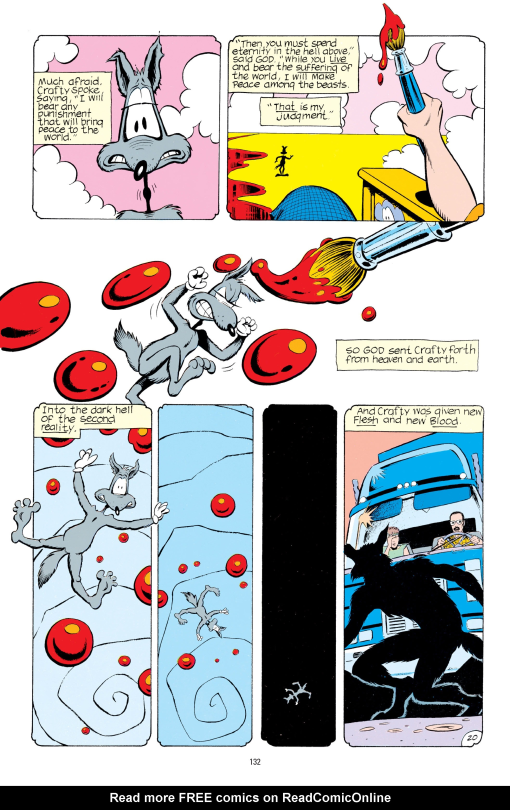
The first movement in this direction is the story about Wile E. Coyote, which sees him rebel against God for creating a life of ceaseless violence for cartoon animals - only to be punished by incarnating him as a werewolf in the real world. Over the course of that story, Wile E. Crafty is run over, shot, crushed, and blown up, becoming a kind of Jesus-like figure whose suffering is supposed to save the animals. It’s a wonderfully batshit idea, and it works well in context - apparently this comic sold like mad so Morrison was encouraged to take it further. Animal Man’s role in this story - as in quite a lot of stories - is to witness Crafty’s death.
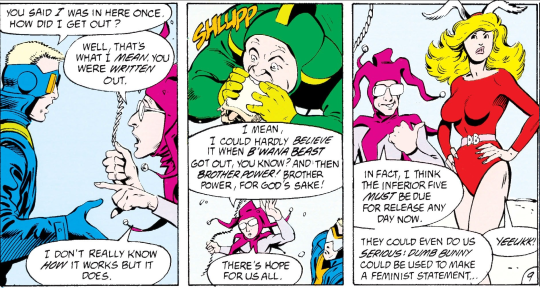
Thus over the course of Animal Man, we encounter a pair of aliens who find that the general trends in comic writing of the day - the emphasis on more complex characterisation for example - is increasingly straining the fabric of fictional reality…

The aliens stage an intervention to try and use Buddy’s memories to repair the timeline (or something??), but this ends up unleashing more chaos down the line, as more and more characters start attaining a fourth-wall breaking awareness. The next arc sets up some unexplained weirdness: a strange ghostly figure of Buddy attempts to communicate with his family, while meanwhile we’re introduced to the character of Highwater, a Native physicist who’s drawn into the mystery of an Arkham Asylum patient who seems to (for our outside eyes) have fourth-wall breaking knowledge.
So after the incident with the aliens, Buddy meets up with Highwater, and they go into the desert and have a peyote trip which leads to some fun imagery, hero gets power up. Meanwhile, government/corporate goons kill Buddy’s family. He gets back, and we find out the cause of the ghostly Buddy: distraught, he tries to time travel back to save them, but when his means of time travel doesn’t make that possible. The guy from Arkham Asylum meanwhile summons a bunch of DC characters from various discarded storylines and alternate universes; the aliens intervene, and Highwater ends up sealing it all off again, in the process becoming a mute Arkham inmate.
Buddy demands answers from the aliens, but they peace out; nevertheless he finds a strange door which takes him to a metafictional plane where he can - much like good old Crafty! - go and demand explanation from his creator. He soon finds discarded fictional characters in a realm where nothing can form stories, and is given a dying monkey with a typewriter that’s writing the comics script, and instructed to carry the monkey to the mythical city of ‘Formation’. (So I guess it’s still kind of animal related!)
But like all the other people Buddy couldn’t save, the monkey dies, and his journey takes him back to the start. After all this he finally gets to meet Grant Morrison!
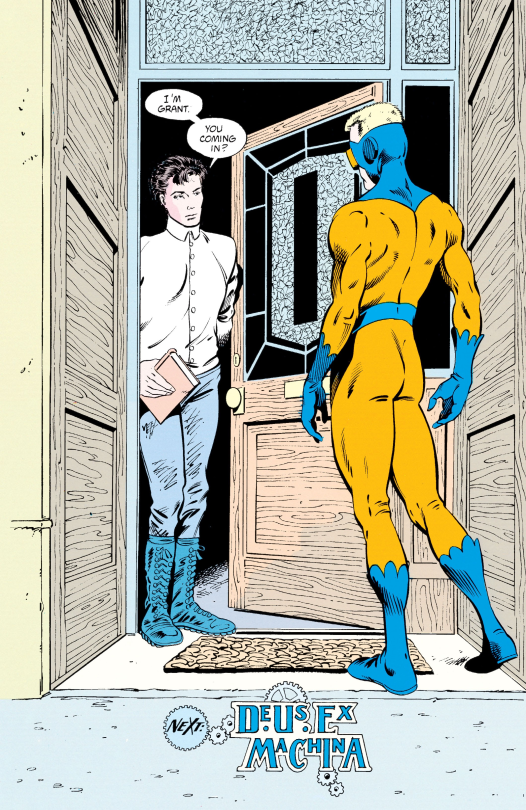
The final issue has Morrison talking to both Buddy and the reader - giving acknowledgements, telling the story of their childhood imaginary friend Foxy, and explaining the craft of comics-making to Buddy and musing on the differences between comics life and real life.
Which is a fun little dialogue, because while it is drawing our attention to the constructed and arbitrary nature of everything in the story, it also at the same time has to function as a story. Buddy’s reactions - panicked incomprehension, questioning - have to continue to feel natural. Even though the comic is turning to us and saying ‘this man is fake’, it does its level best to cue us to think he’s real.
I like metafiction, but after you’ve handled the ‘character discovers they’re fictional’ scene, you need to figure out what it’s actually for. In this case, it’s part of the comic’s general theme of powerlessness and futility. Here’s the key page:

…which literally leads to a panel where Morrison turns to the camera and tells you to join PETA, something that hasn’t aged especially well. Morrison agonises a bit over why we use real death and suffering as entertainment - why they’d think about using their own cat’s death as material for this story - and then leaves, resurrecting Buddy’s family on the final panel.
So! Long summary over (thanks for bearing with me, I wanted to get it all straight in my head).
At this point, ‘fictional characters discover they are fictional’ is a pretty heavily done narrative, so you have to have some kind of very strong reason to use the device. I think that was way less true in the 80s - Italo Calvino’s novel If on a winters night a traveler was only published ‘79 after all!
In this case, its use is to provide a little reflective monologue on 1. living in a cruel and nihilistic world, in contrast to fictional characters who have a creator they can confront 2. Morrison’s position as an outside writer being pulled into the vast machine of the DC universe. Their intervention is… an interesting kind of critical, seeking to update rather than simply write out dubious past storylines, so the story acts as a kind of critical commentary on its predecessors. This is most apparent in one storyline which sees the old character B’wana Beast, a Tarzan-like figure who gets animal powers from a special helmet and is known as the ‘White God’, passing on his powers to a Black anti-apartheid activist. A lot of others simply deal with nostalgia, getting older, the world moving on and becoming more complicated.
Morrison describes their final storyline as an anticlimax. Which like… on the one hand, how could it possibly be? Buddy has uncovered the truth that no character in the setting can know. But on the other hand, by heavily emphasising everything is arbitrary, it does indeed dismantle the tension; there is no way it could be anything other than a final storyline.
Buddy spends much of his narrative under Morrison being unable to do more than stand by as terrible things happen around him. He tries extremely hard to be caring and empathetic, and this is often appreciated but rarely enough to save anyone. In the end he ‘realises’ that ‘he’ has even less power than that - he’s just an instrument of Morrison and whichever next writer (who would apparently choose to turn it into a story about quantum mechanical weirdness, but I stopped at the end of Morrison’s run) so not only are his efforts futile, even his motivation is also not under his control. All pretty solid as far as ‘pseudo-existential’ stories (in Buddy’s words) go.
And yet, as Morrison notes in their conversation, ‘Buddy’ will likely outlive Morrison themselves. To elaborate on that, we can see the figure of ‘Buddy’ conjured in our minds by the prompt of this book lasting as long as it continues to be printed, read, and iterated on - a meme, egregore, etc. etc.. This is the very hollow form of ‘life’ given to dead people who pass into memory, but it isn’t nothing; to create a character who’s not forgotten is quite an achievement.
Morrison’s theme of limited, even disabled characters for whom things never seem to go quite right is the whole impetus of Doom Patrol, so I guess I’ll pick up this thread when I finish digesting that one. Even so early in their career, they’re a very witty writer with a real knack for coming up with compelling, thematic scenarios and convincing characterisation. (Morrison had been writing comics in the UK for 5-6 years before that, so it’s hardly like this is the first time they wrote for a comic, but they were still younger than me at the point they began Animal Man.)
All in all, Animal Man is a compelling story that still holds up very well in 2022. If you want to read it, ComicExtra has the most complete collection of scans I found - scroll down to the 30th anniversary deluxe edition, which is annoyingly uploaded in reverse order.
Next up we’ll be doing a manga! I recently caught up with the absolutely delightful Witch Hat Atelier by Kamome Shirohama, and I can’t wait to dig into all the brilliant techniques she’s using in the art of this manga. See you then.
Comments